莫队
分块简介
对序列进行根号n的拆分,接下来每一段做懒标记和单独处理,对于跨块的操作可以对整个大块进行操作,对于小块我们直接暴力修改,因此时间复杂度可以降低至m*根号n。
基本线段树改分块
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5+10,M = 350;
int n,m,len;
LL add[M],sum[M];
int w[N];
inline int get(int i) {return (i-1)/len;}
void change(int l,int r,int d)
{
if(get(l)==get(r))
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) w[i]+=d,sum[get(i)]+=d;
else{
int i=l,j=r;
while(get(i)==get(l)) w[i]+=d,sum[get(i)]+=d,i++;
while(get(j)==get(r)) w[j]+=d,sum[get(j)]+=d,j--;
for(int k=get(i);k<=get(j);k++) sum[k]+=len*d,add[k]+=d;
}
}
LL query(int l,int r)
{
LL res=0;
if(get(l)==get(r))
{
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) res+=w[i]+add[get(i)];
return res;
}
else{
int i=l,j=r;
while(get(i)==get(l)) res+=w[i]+add[get(i)],i++;
while(get(j)==get(r)) res+=w[j]+add[get(j)],j--;
for(int k=get(i);k<=get(j);k++) res+=sum[k];
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
len=sqrt(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&w[i]);
sum[get(i)]+=w[i];
}
char op[2];
int l,r,d;
while(m--)
{
scanf("%s%d%d",op,&l,&r);
if(*op=='C')
{
scanf("%d",&d);
change(l,r,d);
}
else printf("%lld\n",query(l,r));
}
return 0;
}基础莫队
莫队是一种离线算法,他的思想是对双指针的进一步优化,利用分块的思想进行优化,一般可以解决对状态比较好维护的序列,可以进行O(1)的操作,或者利用回滚莫队进行回滚。
求区间的子区间中不同数的个数。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e4+10,M = 2e5+10,S = 1000010;
int n,m,len;
int w[N],ans[M];
struct Query{
int id,l,r;
}q[M];
int cnt[S];
inline int get(int x) {return x/len;}
bool cmp(const Query&a,const Query&b)
{
int i=get(a.l),j=get(b.l);
if(i!=j) return i<j;
return a.r<b.r;
}
void add(int x,int &res)
{
if(!cnt[x]) res++;
cnt[x]++;
}
void del(int x,int &res)
{
cnt[x]--;
if(!cnt[x]) res--;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&w[i]);
scanf("%d",&m);
len=sqrt((double)n);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int l,r;
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
q[i]=(Query){i,l,r};
}
sort(q,q+m,cmp);
for(int k=0,i=0,j=1,res=0;k<m;k++)
{
int id=q[k].id,l=q[k].l,r=q[k].r;
while(i<r) add(w[++i],res);
while(i>r) del(w[i--],res);
while(j<l) del(w[j++],res);
while(j>l) add(w[--j],res);
ans[id]=res;
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}带修改的莫队
在上题的基础上加上了修改的操作,引入了时间戳的概念,我们可以利用对时间戳增加另一个维度来维持修改询问。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4+10,S = 1e6+10;
int n,m,mq,mc,len;
int w[N],cnt[S],ans[N];
struct Query{
int id,l,r,t;
}q[N];
struct Modift{
int p,c;
}c[N];
inline int get(int x) {return x/len;}
bool cmp(const Query& a,const Query& b)
{
int al=get(a.l),ar=get(a.r);
int bl=get(b.l),br=get(b.r);
if(al!=bl) return al<bl;
if(ar!=br) return ar<br;
return a.t<b.t;
}
void add(int x,int &res)
{
if(!cnt[x]) res++;
cnt[x]++;
}
void del(int x,int &res)
{
cnt[x]--;
if(!cnt[x]) res--;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&w[i]);
while(m--)
{
char op[2];
int a,b;
scanf("%s%d%d",op,&a,&b);
if(*op=='Q') mq++,q[mq]=(Query){mq,a,b,mc};
else mc++,c[mc]=(Modift){a,b};
}
len = cbrt((double)n * max(1 , mc));
sort(q+1,q+mq+1,cmp);
for(int i=0,j=1,t=0,k=1,res=0;k<=mq;k++)
{
int id=q[k].id,l=q[k].l,r=q[k].r,tm=q[k].t;
while(i<r) add(w[++i],res);
while(i>r) del(w[i--],res);
while(j<l) del(w[j++],res);
while(j>l) add(w[--j],res);
while(t<tm)
{
t++;
if(c[t].p>=j&&c[t].p<=i)
{
del(w[c[t].p],res);
add(c[t].c,res);
}
swap(w[c[t].p],c[t].c);
}
while(t>tm)
{
if(c[t].p>=j&&c[t].p<=i)
{
del(w[c[t].p],res);
add(c[t].c,res);
}
swap(w[c[t].p],c[t].c);
t--;
}
ans[id]=res;
}
for(int i=1;i<=mq;i++) printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}回滚莫队
如上所示的莫队都是对于单点修改的比较简洁的莫队,但是有些时候修改可能就不利于操作,比如需要维护状态最值的问题,在区间加入值的时候我们可以直接迭代,但是对于减少元素的时候,我们就难于更改。在排序的时候我们的右端点是递增的,所以我们可以对于同一块内的区间直接暴力,时间是根号n;对于块间我们首先把最左快的进行暴力处理,对于右边的块我们严格递增即可。时间复杂度是n根号n。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int n,m,len;
int w[N],cnt[N];
LL ans[N];
struct Query{
int id,l,r;
}q[N];
vector<int> nums;
inline int get(int x){return x/len;}
bool cmp(const Query& a,const Query& b)
{
int i=get(a.l),j=get(b.l);
if(i!=j) return i<j;
return a.r<b.r;
}
void add(int x,LL &res)
{
cnt[x]++;
res=max(res,(LL)cnt[x]*nums[x]);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
len=sqrt(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&w[i]),nums.push_back(w[i]);
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
nums.erase(unique(nums.begin(),nums.end()),nums.end());
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
w[i]=lower_bound(nums.begin(),nums.end(),w[i])-nums.begin();
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int l,r;
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
q[i]=(Query){i,l,r};
}
sort(q,q+m,cmp);
for(int x=0;x<m;)
{
int y=x;
while(y<m&&get(q[y].l)==get(q[x].l)) y++;
int right=get(q[x].l)*len+len-1;
while(x<y&&q[x].r<right)
{
LL res=0;
int id=q[x].id,l=q[x].l,r=q[x].r;
for(int k=l;k<=r;k++) add(w[k],res);
ans[id]=res;
for(int k=l;k<=r;k++) cnt[w[k]]--;
x++;
}
LL res=0;
int i=right,j=right+1;
while(x<y)
{
int id=q[x].id,l=q[x].l,r=q[x].r;
while(i<r) add(w[++i],res);
LL backup=res;
while(j>l) add(w[--j],res);
ans[id]=res;
while(j<right+1) cnt[w[j++]]--;
res=backup;
x++;
}
memset(cnt,0,sizeof cnt);
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) printf("%lld\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}树上莫队
对于树上的路径对于莫队来说一般用的是欧拉序列的应用,欧拉序列是指对树进行dfs遍历,在dfs前输出一次,在回溯后再输出一次。对于LCA可以利用倍增也可以用tarjan,在线或者离线的利用。本题是求树上的路径的不同值个数。
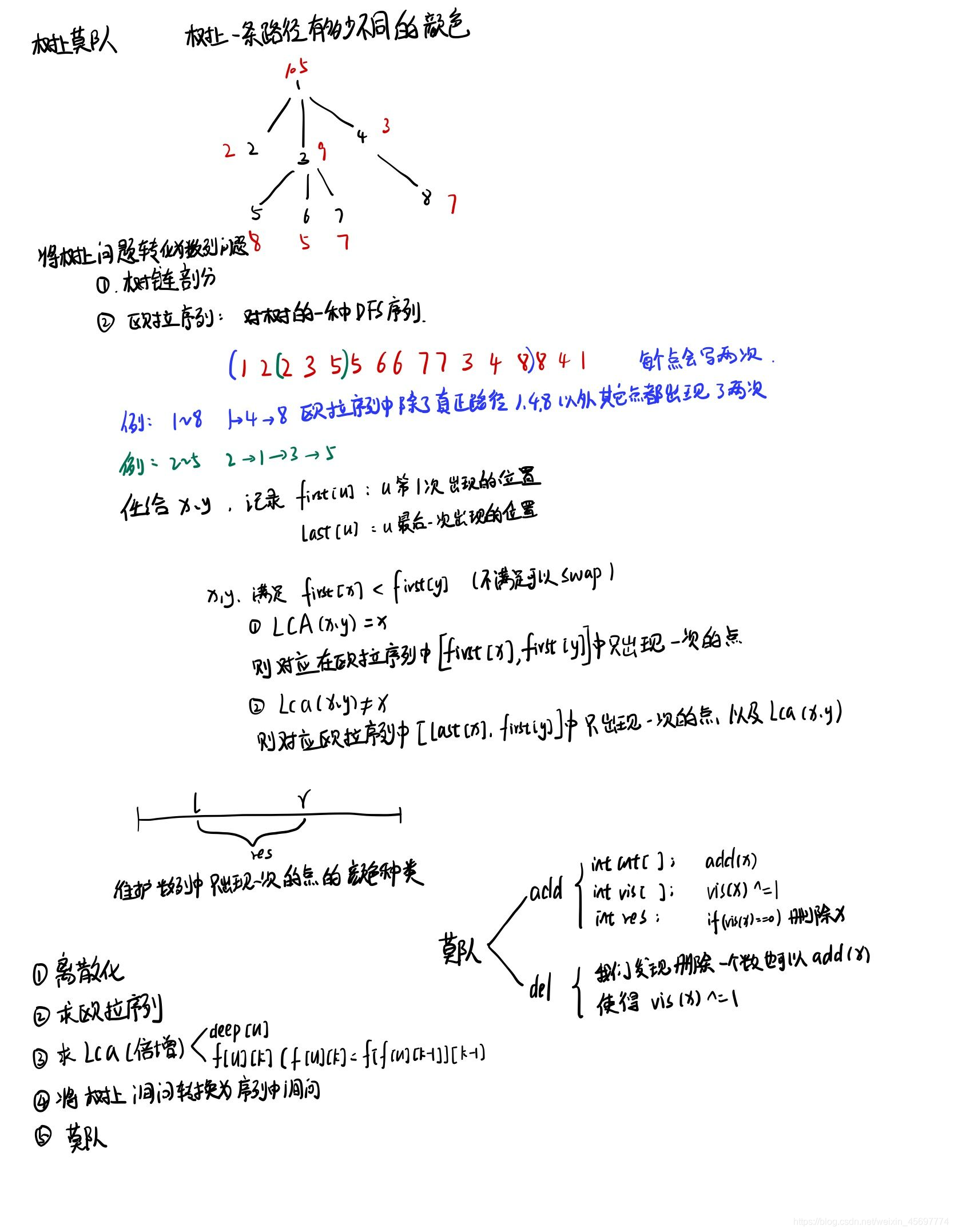
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int w[N];
int n,m,len;
int head[N],idx;
int depth[N],f[N][16];
int seq[N],first[N],last[N],top;
int cnt[N],st[N],ans[N];
int que[N];
struct Edge{
int next,to;
}edge[N];
struct Query{
int id,l,r,p;
}q[N];
vector<int> nums;
void add_edge(int a,int b) {
edge[idx]=(Edge){head[a],b},head[a]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int u,int father)
{
seq[++top]=u;
first[u]=top;
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=edge[i].next)
{
int j=edge[i].to;
if(j!=father) dfs(j,u);
}
seq[++top]=u;
last[u]=top;
}
void bfs()
{
memset(depth,0x3f,sizeof depth);
depth[0]=0,depth[1]=1;
int hh=0,tt=0;
que[0]=1;
while(hh<=tt)
{
int t=que[hh++];
for(int i=head[t];~i;i=edge[i].next)
{
int j=edge[i].to;
if(depth[j]>depth[t]+1)
{
depth[j]=depth[t]+1;
f[j][0]=t;
for(int k=1;k<=15;k++)
f[j][k]=f[f[j][k-1]][k-1];
que[++tt]=j;
}
}
}
}
int lca(int a,int b)
{
if(depth[a]<depth[b]) swap(a,b);
for(int k=15;k>=0;k--)
if(depth[f[a][k]]>=depth[b])
a=f[a][k];
if(a==b) return a;
for(int k=15;k>=0;k--)
if(f[a][k]!=f[b][k])
{
a=f[a][k];
b=f[b][k];
}
return f[a][0];
}
inline int get(int x) {return x/len;}
bool cmp(const Query& a,const Query& b)
{
int i=get(a.l),j=get(b.l);
if(i!=j) return i<j;
return a.r<b.r;
}
void add(int x,int &res)
{
st[x]^=1;
if(!st[x])
{
cnt[w[x]]--;
if(!cnt[w[x]]) res--;
}
else{
if(!cnt[w[x]]) res++;
cnt[w[x]]++;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&w[i]),nums.push_back(w[i]);
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
nums.erase(unique(nums.begin(),nums.end()),nums.end());
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
w[i]=lower_bound(nums.begin(),nums.end(),w[i])-nums.begin();
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
add_edge(a,b),add_edge(b,a);
}
dfs(1,-1);
bfs();
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(first[a]>first[b]) swap(a,b);
int p=lca(a,b);
if(a==p) q[i]={i,first[a],first[b]};
else q[i]={i,last[a],first[b],p};
}
len=sqrt(top);
sort(q,q+m,cmp);
for(int i=0,L=1,R=0,res=0;i<m;i++)
{
int id=q[i].id,l=q[i].l,r=q[i].r,p=q[i].p;
while(R<r) add(seq[++R],res);
while(R>r) add(seq[R--],res);
while(L<l) add(seq[L++],res);
while(L>l) add(seq[--L],res);
if(p) add(p,res);
ans[id]=res;
if(p) add(p,res);
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}
